Dr. J. Robert Oppenheimer
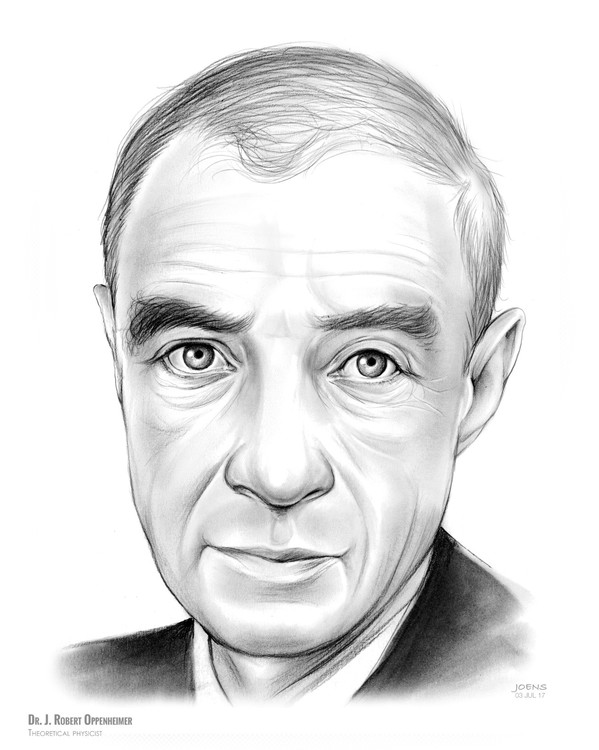
Dr. J. Robert Oppenheimer Pencil Sketch of the Day for Monday, July 3, 2017 Julius Robert Oppenheimer (April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physicist and professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley. Oppenheimer was the wartime head of the Los Alamos Laboratory and is among those who are credited with being the "father of the atomic bomb" for their role in the Manhattan Project, the World War II undertaking that developed the first nuclear weapons used in the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The first atomic bomb was detonated on July 16, 1945, in the Trinity test in New Mexico; Oppenheimer later remarked that it brought to mind words from the Bhagavad Gita: "Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds." After the war, Oppenheimer became chairman of the influential General Advisory Committee of the newly created United States Atomic Energy Commission. He used that position to lobby for international control of nuclear power to avert nuclear proliferation and a nuclear arms race with the Soviet Union. After provoking the ire of many politicians with his outspoken opinions during the Second Red Scare, he suffered the revocation of his security clearance in a much-publicized hearing in 1954, and was effectively stripped of his direct political influence; he continued to lecture, write and work in physics. Nine years later, President John F. Kennedy awarded (and Lyndon B. Johnson presented) him with the Enrico Fermi Award as a gesture of political rehabilitation. Oppenheimer's achievements in physics included the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for molecular wave functions, work on the theory of electrons and positrons, the Oppenheimer–Phillips process in nuclear fusion, and the first prediction of quantum tunneling. With his students he also made important contributions to the modern theory of neutron stars and black holes, as well as to quantum mechanics, quantum field theory, and the interactions of cosmic rays. As a teacher and promoter of science, he is remembered as a founding father of the American school of theoretical physics that gained world prominence in the 1930s. After World War II, he became director of the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. Source: Wikipedia